
最近有个客户端的需求是和服务端建立安全的链路,需要用ssl双向认证的方式实现。刚开始的时候被各种证书认证搞得晕乎乎-_-,花了好长时间才理清思路实现需求,所以写下这篇文章记录分享。先介绍下啥是SSL,后面给出demo源码。
参考https://blog.csdn.net/wuliganggang/article/details/78428866
https://blog.csdn.net/duanbokan/article/details/50847612
https://blog.csdn.net/zhangtaoym/article/details/55259889
SSL是安全套接层(secure sockets layer),而TLS是SSL的继任者,叫传输层安全(transport layer security)。是为网络通信提供安全及数据完整性的一种安全协议。TLS与SSL在传输层对网络连接进行加密。
比如如HTTP协议是明文传输,加上SSL层之后,就有了雅称HTTPS。它的发展依次经历了下面几个时期
SSL1.0: 已废除
SSL2.0: RFC6176,已废除
SSL3.0: RFC6101,基本废除
TLS1.0: RFC2246,目前大都采用此种方式
TLS1.1: RFC4346
TLS1.2: RFC5246,没有广泛使用
TLS1.3: RFC 8446,于2018年8月发表
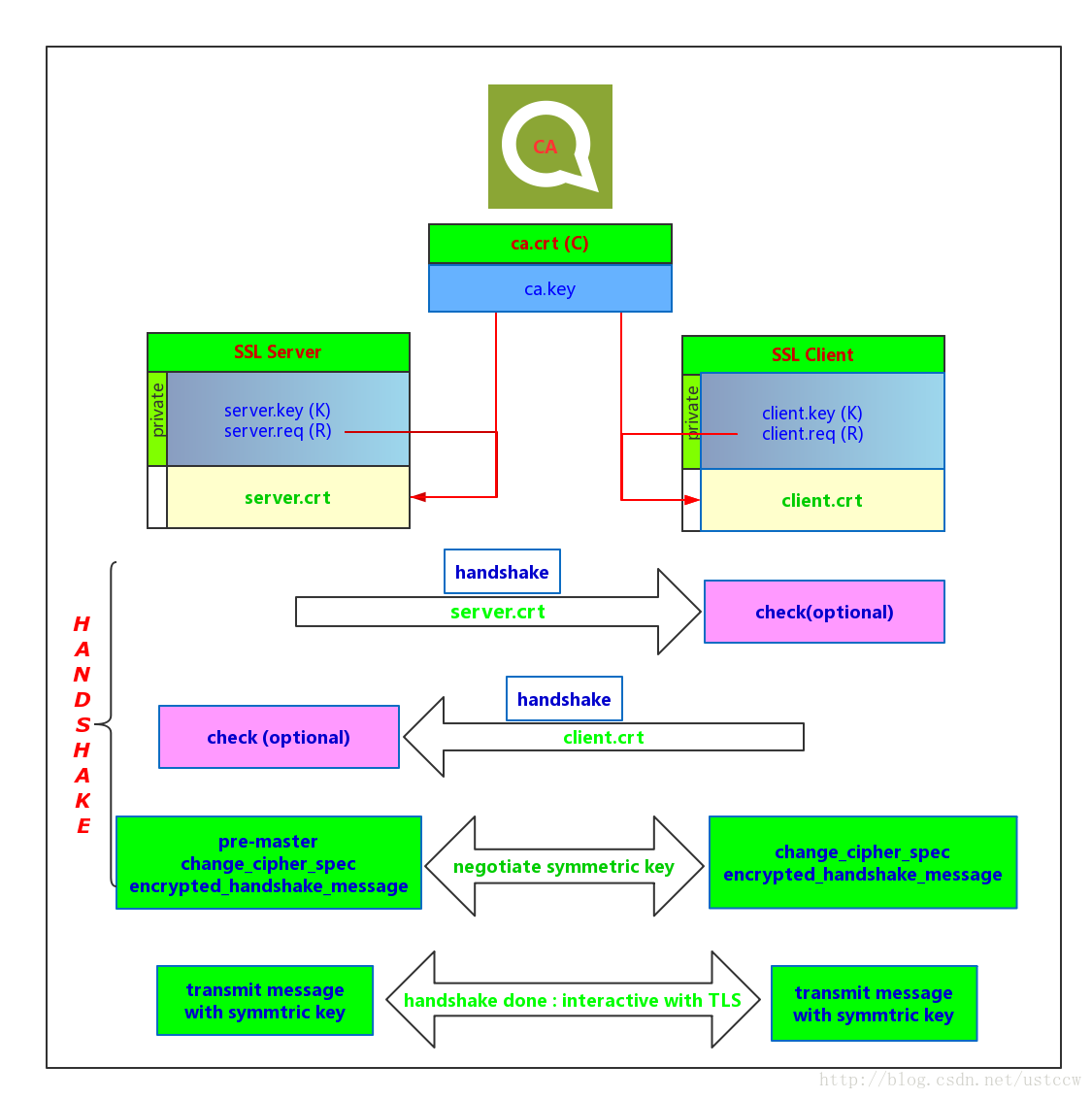
CA: 证书授权中心( certificate authority)。 它呢,类似于国家出入境管理处一样,给别人颁发护照;也类似于国家工商管理局一样,给公司企业颁发营业执照。
它有两大主要性质:
SSL/TLS协商的过程可以参考这篇文章SSL/TLS协商过程详解
证书生成# * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright# notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the# documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.# * Neither the name of the axTLS project nor the names of its# contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived# from this software without specific prior written permission.## THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS# "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT# LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR # A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR# CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,# SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED# TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,# DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY # OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING# NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF# THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.### Generate the certificates and keys for testing.#PROJECT_NAME="TLS Project"# Generate the openssl configuration files.cat > ca_cert.conf << EOF [ req ]distinguished_name = req_distinguished_nameprompt = no[ req_distinguished_name ] O = $PROJECT_NAME Dodgy Certificate AuthorityEOFcat > server_cert.conf << EOF [ req ]distinguished_name = req_distinguished_nameprompt = no[ req_distinguished_name ] O = $PROJECT_NAME CN = 192.168.111.100EOFcat > client_cert.conf << EOF [ req ]distinguished_name = req_distinguished_nameprompt = no[ req_distinguished_name ] O = $PROJECT_NAME Device Certificate CN = 192.168.111.101EOFmkdir camkdir servermkdir clientmkdir certDER# private key generationopenssl genrsa -out ca.key 1024openssl genrsa -out server.key 1024openssl genrsa -out client.key 1024# cert requestsopenssl req -out ca.req -key ca.key -new \ -config ./ca_cert.confopenssl req -out server.req -key server.key -new \ -config ./server_cert.conf openssl req -out client.req -key client.key -new \ -config ./client_cert.conf # generate the actual certs.openssl x509 -req -in ca.req -out ca.crt \ -sha1 -days 5000 -signkey ca.keyopenssl x509 -req -in server.req -out server.crt \ -sha1 -CAcreateserial -days 5000 \ -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.keyopenssl x509 -req -in client.req -out client.crt \ -sha1 -CAcreateserial -days 5000 \ -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.keyopenssl x509 -in ca.crt -outform DER -out ca.deropenssl x509 -in server.crt -outform DER -out server.deropenssl x509 -in client.crt -outform DER -out client.dermv ca.crt ca.key ca/mv server.crt server.key server/mv client.crt client.key client/mv ca.der server.der client.der certDER/rm *.confrm *.reqrm *.srl做如下修改,终端执行。

server
from flask import Flaskapp = Flask(__name__)@app.route('/')def hello_world(): return 'Hello World!'if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=True, ssl_context=('server.crt', 'server.key'))client
import urllib.requestimport sslif __name__ == '__main__': CA_FILE = "ca.crt" context = ssl.SSLContext(ssl.PROTOCOL_TLS) context.check_hostname = False context.load_verify_locations(CA_FILE) context.verify_mode = ssl.CERT_REQUIRED try: request = urllib.request.Request('https://127.0.0.1:5000/') res = urllib.request.urlopen(request, context=context) print(res.code) print(res.read().decode("utf-8")) except Exception as ex: print("Found Error in auth phase:%s" % str(ex))https的测试本来使用使用浏览器,只要将ca证书安装到本地就可能使用浏览器访问,但是因为认证过程需要检测验证hostname,测试使用的自签名证书信息是随意填写的,所以即使安装了证书浏览器也会提示链接不安全。所以客户端使用ssl模块的load_verify_locations()方法加载根证书,并且将check_hostname设置为False。
双向认证https版本
server
client
import urllib.requestimport sslif __name__ == '__main__': CA_FILE = "ca.crt" KEY_FILE = "client.key" CERT_FILE = "client.crt" context = ssl.SSLContext(ssl.PROTOCOL_TLS) context.check_hostname = False context.load_cert_chain(certfile=CERT_FILE, keyfile=KEY_FILE) context.load_verify_locations(CA_FILE) context.verify_mode = ssl.CERT_REQUIRED try: # 通过request()方法创建一个请求: request = urllib.request.Request('https://127.0.0.1:5000/') res = urllib.request.urlopen(request, context=context) print(res.code) print(res.read().decode("utf-8")) except Exception as ex: print("Found Error in auth phase:%s" % str(ex))socket版本
server
client
import socketimport sslclass client_ssl: def send_hello(self,): CA_FILE = "ca.crt" KEY_FILE = "client.key" CERT_FILE = "client.crt" context = ssl.SSLContext(ssl.PROTOCOL_TLS) context.check_hostname = False context.load_cert_chain(certfile=CERT_FILE, keyfile=KEY_FILE) context.load_verify_locations(CA_FILE) context.verify_mode = ssl.CERT_REQUIRED # 与服务端建立socket连接 with socket.socket() as sock: # 将socket打包成SSL socket with context.wrap_socket(sock, server_side=False) as ssock: ssock.connect(('127.0.0.1', 5678)) # 向服务端发送信息 msg = "do i connect with server ?".encode("utf-8") ssock.send(msg) # 接收服务端返回的信息 msg = ssock.recv(1024).decode("utf-8") print(f"receive msg from server : {msg}") ssock.close()if __name__ == "__main__": client = client_ssl() client.send_hello()ssl认证主要用到python的ssl模块,如果有不清楚的也可以自己阅读下官方文档。
| 通信人家园 (https://www.txrjy.com/) | Powered by C114 |